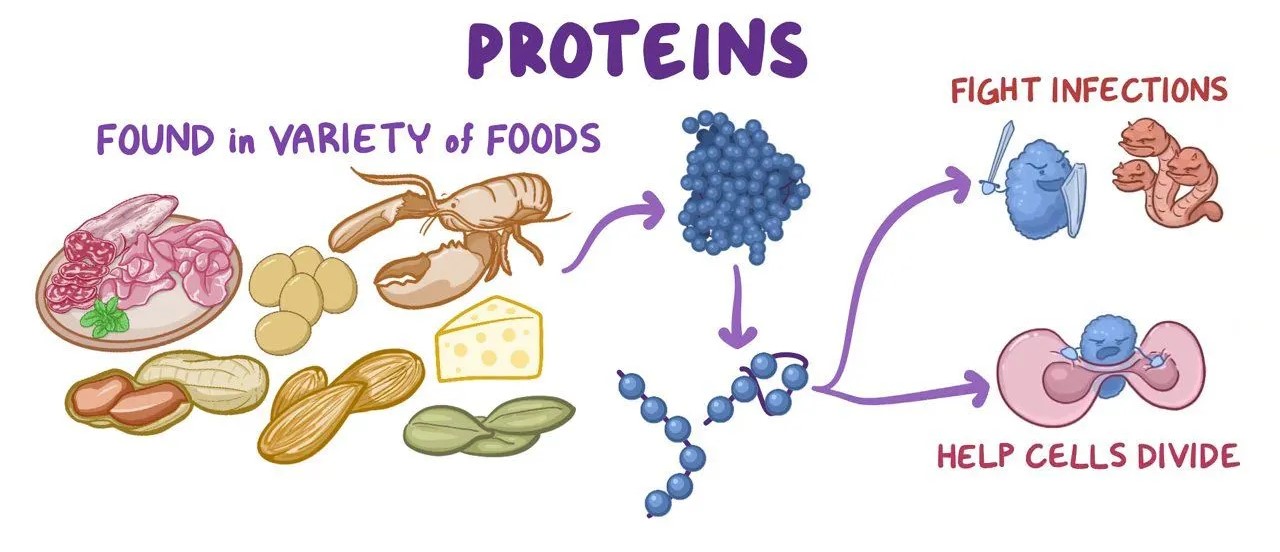
Proteins: The Worker Bees of the Body
The World of Proteins are like worker bees in that they work tirelessly to keep us up and running, so it is no wonder why we need them as much as our bodies rely on air. From muscle growth to the health of your brain, they are essential. These are large molecules composed mainly of amino acids and used for building cells, repairing tissues, and other functions in the body. Everything from your muscles healing after a workout to the way that you think is due to proteins.
What Are Proteins?
Proteins are large, complex molecules and play many critical roles in the body. These make up the muscle, skin, organs, and structures of your body. The body could not develop, fix itself, or perform its functions without them. Proteins are like the scaffolding doing all of this work.
Function:
Proteins, other than providing structural support, serve as enzymes and hormones in the human body. They also play a key role in certain chemotherapeutic reactions occurring within the human form. Regulating metabolism, carrying oxygen through hemoglobin…Proteins do everything to make sure each and every biological process goes well. Proteins are always working away behind the scenes, whatever the task.
When it comes to the building blocks of life, biologists often say proteins are crucial for good reason. They heal injuries, govern cellular functions, and control our flow of blood. Without enough protein, the body struggles to heal wounds or recover from illnesses and may begin breaking down muscle mass for amino acids. They are not only crucial, but they also have proven to be irreplaceable.
Healthy Proteins vs. Unhealthy Proteins: What You Need To Know
There are good and bad proteins, so make sure you choose the right one…. Some are good for health, while some can be bad if overconsumed. Knowing the difference between good and bad proteins is essential in ensuring your best diet for lifelong health.
What Are Good Proteins?
Eat whole + unprocessed for the good proteins. Most of these needed proteins can be found in lean meats, fish, eggs, and dairy products, as well they are also plant-sourced from legumes and quinoa. Animal sources are complete proteins and contain all nine of the essential amino acids. Incomplete proteins, which are most often found in plant sources, do not contain all of the necessary amino acids but can be paired to create complete proteins.
Foods that contain Complete Proteins:
Foods like chicken, beef, and eggs are all complete proteins. They provide all the essential amino acids found in proteins. These plant-based proteins are considered incomplete because they do not contain all of the nine essential amino acids that humans need to get from their diet; seeds and grains, for example. Eating a diet rich in variety is the key to consuming all necessary nutrients.
Whereas animal-based proteins are commonly believed to be more “complete,” plant-based proteins have found an ever-growing niche in the market between consumers wanting a healthier lifestyle. Protein-rich and low in harmful saturated fats are foods like tofu, lentils, and quinoa. They contain dietary fiber that aids digestion and benefits heart health as well.
The Bad Kind
Not all proteins are good for the body. For example, highly-processed proteins, such as those in some deli meats and fast foods, may increase the chance of developing heart disease. Additionally, an overconsumption of red or processed meat inflames the body and may cause other chronic diseases. Quality matters just as much as quantity; here are some processed proteins and what they are good for.
When Convenience Can Be Life-Threatening
Foods like processed meats, bacon or sausages, and certain deli slices contain a lot of preservatives and salt. Consequently, such foods increase the chances of developing cancer or heart disease. Therefore, the risks heavily outweigh the benefits of such proteins, and they should be exclusively minimized.
Bad Effects Of Bad Proteins
Overconsumption of protein, especially from animal sources, may strain your kidneys, cause dehydration, and promote bone loss. Moderation is key. Plant-based alternatives should complement your protein consumption. When the body is balanced, you absorb only as much as you need, without added stress to vital organs.
Understand How Proteins React in Our Bodies – From Muscle to Brain
Once ingested, the body breaks down protein into amino acids that help build or repair tissues. Amino acids expand the size of muscles by allowing muscle fibers to grow. Some amino acids – like tryptophan and tyrosine – found in proteins are turned into dopamine or serotonin, which are related to mood regulation.
Proteins Building Muscles
When the body exercises, especially when lifting heavy weights or resistance training, muscles suffer small tears in their fibers. Amino acids repair these tears, rebuilding and generating muscle gain in a process called hypertrophy.
Protein and the Brain: How It Impacts Cognition
Essential proteins are also needed for brain function and neurotransmitter production. Neurotransmitters are chemical messengers that help brain cells communicate. Tryptophan is necessary for creating serotonin, and tyrosine is needed for dopamine, while dopamine is necessary for motivation and focus.
Protein and Tissue Repairs
When the body is injured or sick, the proteins act quickly. Collagen helps with the “scab” and is essential for wound regeneration. Then it makes cells and tissues and helps boost the immune system. Providing high-quality proteins helps victims heal quicker, while low-quality proteins result in higher downtime.
The Science Behind Protein And Fitness
Protein is a building block of fitness, and it is most important for anyone trying to gain muscle. As the muscles tear due to the gym, proteins play a part in it. Proteins provide the hypertrophy of muscles.
Best Sources For Or Recommended
When it comes to hypertrophy, some proteins are more important than others. The best sources of protein are animal-based, which contain essential amino acids and are easily digestible.
Whey
Whey protein is best for recovery. Because it has the fastest digestion time, it is recommended to take it immediately after training. Supplements exist because of the need for immediate protein straight after the gym to speed recovery. It has all necessary amino acids, including BCAA, for rapid recovery and initiating hypertrophy.
Casein
Casein is a slow-digesting protein. It is recommended to be eaten before bedtime, and aminos help the body indirectly through the night.
Plant Sources – Building Muscle
They contain a low amount of proteins. The single approach was combining sources like pea, hemp, and rice protein because they don’t have a whole amino acid profile alone. Many vegan bodybuilders use plant sources to achieve hypertrophy.
Protein Supplement for Muscle Repair Post-Workout
After a brutal exercise session, your muscles require protein to initiate repair. Eating protein within the first 30 minutes of your workout ensures that they are supplied right away to those muscular tissues. This “anabolic window,” where protein synthesis is at its peak, is essential to recover faster and make amazing gains.
Muscles are made up of fast-twitch and slow-twitch muscle fibers. Each one responds differently to exercise and has variations in the amounts of protein needed for peak performance.
How Muscle Fiber Types Work
Fast-twitch fibers get activated for short bursts of power, such as in sprints or heavy lifting workouts, and slow-twitch fibers are engaged during endurance activities like long runs. These fibers have different metabolic requirements and need distinct forms of protein support for healing and growth.
Fast-Twitch Muscles: Protein for Power
Fast-twitch fibers rely on anaerobic energy and fatigue quickly. You need a fast-acting protein source rich in Branched-Chain Amino Acids (BCAAs), like whey, to support rapid repair and growth post-exercise.
Slow-Twitch Muscles: Protein for Endurance and Stamina
Slow-twitch muscle fibers, which support endurance activities, require continued protein support. Casein protein works well here due to its slow digestion rate. Casein gradually supplies amino acids over time, maintaining muscle mass during long exercise sessions, such as marathon training.
Proteins for Injury Recovery and Illness Management
Besides being essential building blocks for muscles, proteins help us recover from injuries and manage illnesses effectively. Proteins repair muscles and tissues, build new cells, and support the immune system, allowing the body to heal faster.
Proteins Help Repair Injury
When injured, the body uses protein to repair and rebuild torn tissue. Collagen and other proteins play a pivotal role in regenerating skin, tendons, and ligaments, helping the body heal faster. High-protein diets are often recommended for athletes recovering from surgery or injury.
Proteins in Treatment of Chronic Illnesses
Proteins can also assist in managing chronic diseases. For individuals with illnesses such as diabetes or cancer, proteins help preserve muscle mass, support immune function, and aid recovery from treatments like chemotherapy.

7-Day Protein-Supplemented Diet for Muscle Mass
A well-structured diet plan can help someone grow muscle. Bodybuilders usually need between 1.2 to 2.2 grams of protein per kilogram of body weight daily. This ensures a consistent supply of amino acids to the muscles for growth and repair.
Day 1: Focus on High-Quality Animal Proteins
- Breakfast: Egg white omelet with spinach and turkey bacon.
- Lunch: Grilled chicken breast with quinoa and roasted vegetables.
- Dinner: Salmon with sweet potatoes and steamed broccoli.
- Snacks: Greek yogurt with almonds.
Day 2: Incorporating Plant-Based Protein Sources
- Breakfast: Tofu scramble with avocado and whole grain toast.
- Lunch: Lentil salad with mixed greens and vinaigrette.
- Dinner: Black bean burger with a side of couscous and grilled asparagus.
- Snacks: Hummus with carrot sticks.
Day 3: Pre and Post-Workout Protein Strategies
- Pre-Workout: Protein smoothie with banana, peanut butter, and whey protein.
- Post-Workout: Grilled steak with brown rice and green beans.
- Dinner: Shrimp stir-fry with bell peppers and zucchini.
- Snacks: Cottage cheese with berries.
Day 4: Balance of Animal and Plant-Based Proteins
- Breakfast: Scrambled eggs with black beans and salsa.
- Lunch: Grilled chicken salad with avocado and mixed greens.
- Dinner: Lentil soup with a side of quinoa and roasted vegetables.
- Snacks: Edamame with sea salt.
Day 5: Protein-Rich Snacks for Sustained Muscle Growth
- Breakfast: Smoothie with spinach, protein powder, and almond milk.
- Lunch: Tuna salad with whole grain crackers and a side of mixed greens.
- Dinner: Beef stir-fry with brown rice and broccoli.
- Snacks: Protein bars or hard-boiled eggs.
Day 6: High-Protein Meals for Rest and Recovery
- Breakfast: Scrambled tofu with mushrooms and onions.
- Lunch: Chicken breast with wild rice and a side salad.
- Dinner: Grilled salmon with lentils and sautéed kale.
- Snacks: Protein shakes or Greek yogurt.
Day 7: Cheat Day with Protein-Enhanced Options
- Breakfast: Pancakes with protein powder and a side of scrambled eggs.
- Lunch: Grilled chicken sandwich with whole grain bread and a side salad.
- Dinner: BBQ ribs with a baked sweet potato.
- Snacks: Cheese sticks or nuts.
AI is Now Revolutionizing Protein Science to Create the Future of Proteins
Protein structures are responsible for almost everything, and machine learning has been used to predict the structure of a protein—and even create new ones we could ever need.
AI Transforms Protein Discovery
With extensive datasets and advanced algorithms, AI now plays a key role in analyzing protein structures and predicting how they will behave in the body. This drives innovation in drug discovery, enables personalized medicine, and reduces the time for new drugs to reach the market.
Green Fluorescent Protein Game Changer—AI-Version by EvolutionaryScale
EvolutionaryScale, a biotech startup, has developed a new green fluorescent protein using AI. This protein, which glows in the dark like sea creatures, changes everything we know about medical imaging and research. Without AI, developing this protein might have taken millions of years.
AlphaFold and the Protein Folding Breakthrough
DeepMind’s AlphaFold cracked the protein folding problem that researchers have been trying to solve for decades. This opens the door to new treatments for diseases like Alzheimer’s and cancer, as researchers can now model protein folding more accurately and mix them with pharmaceuticals.
Proteins for Future Medical Breakthroughs
As AI advances, proteins will play even more vital roles in future medical innovations. Engineered proteins could potentially treat everything from cancers to drug-resistant bacterial infections, reforming how we approach healthcare.
Engineering New Proteins for Medicine Using AI
AI can now design new or evolved proteins to target specific issues, like combating cancer cells or preventing neurological problems before they manifest. AI-generated proteins could also offer personalized medicine, tailoring drugs to individual needs.
AI’s Potential to Revolutionize Healthcare
AI-generated proteins are already on the horizon and could provide cures for a range of diseases, from autoimmune disorders to genetic conditions that currently have limited treatments.
Fighting Drug-Resistant Bacteria and Cancer with AI-Generated Proteins
AI-generated proteins offer new ways to fight drug-resistant bacteria by designing proteins that attack bacteria in novel ways, creating new antibiotics. Custom proteins might also target and kill cancer cells, offering new hope for treatment.
Health, Fitness & AI Innovation Intersect
Proteins are more than just building blocks for muscles—they’re central to life itself. Whether helping meet fitness goals or reinventing medical treatments through AI, proteins demonstrate their relevance in health and science today. With AI, the possibilities for breakthroughs in protein science seem limitless.

FAQs
Why are proteins called the building blocks of life?
Proteins are responsible for constructing tissues, supporting cellular functions, and facilitating essential biological processes, making them indispensable for life.
Can I build muscle without animal protein?
Yes, plant-based proteins like quinoa, lentils, and tofu can provide sufficient amino acids for muscle growth, especially when combined properly.
How much protein should I consume daily for muscle growth?
Bodybuilders should aim for 1.2 to 2.2 grams of protein per kilogram of body weight each day.
What role do proteins play in brain function?
Proteins help produce neurotransmitters, such as serotonin and dopamine, which regulate mood, cognition, and mental clarity.
How does AI help in creating new proteins?
AI models analyze protein structures and predict how they’ll behave, allowing scientists to design new proteins that can target specific diseases or medical challenges.